Explore the world of psoriasis, an autoimmune skin condition affecting millions Understand its origins, symptoms, and discover practical approaches to managing and improving the quality of life for those with psoriasis
What is psoriasis? Psoriasis is a chronic skin condition that affects millions of individuals worldwide. In this comprehensive guide, we'll delve into the intricacies of psoriasis, exploring its causes, symptoms, risk factors, prevention strategies, and the latest advancements in its treatment. Whether you're someone living with psoriasis, a caregiver, or simply interested in understanding this condition better, this guide aims to provide you with valuable insights into the world of psoriasis.
Understanding Psoriasis: An Overview
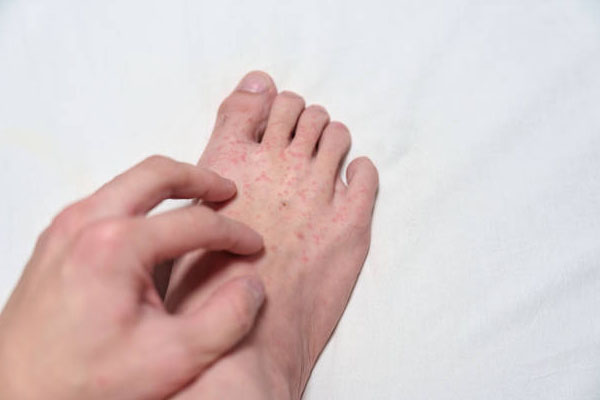
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune skin condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is characterized by the rapid buildup of skin cells, leading to the formation of thick, red, scaly patches on the skin's surface.
Psoriasis can occur on any part of the body, but it most commonly affects the elbows, knees, scalp, and lower back. The condition can cause itching, discomfort, and self-consciousness due to the visibility of the skin lesions.
The exact cause of psoriasis is still unknown. However, it is believed to be related to a combination of genetic, immune system, and environmental factors. Certain triggers, such as stress, infections, injuries, or certain medications, can exacerbate psoriasis symptoms.
Psoriasis is not contagious, which means it cannot be spread from person to person. Although it is a chronic condition with no known cure, various treatment options are available to manage the symptoms effectively and improve the quality of life for individuals with psoriasis.
What is Psoriasis and What are its Common Symptoms?
Psoriasis is a chronic inflammatory skin condition that affects the life cycle of skin cells. It causes cells to build up rapidly on the surface of the skin, leading to the formation of thick, red, and scaly patches known as plaques.
Psoriasis can occur on any part of the body, but it typically affects the elbows, knees, scalp, and lower back. The severity of the condition can vary from person to person, with some individuals experiencing mild symptoms and others having more severe manifestations.
The common symptoms of psoriasis include:
- Red patches of skin: These patches are often covered with thick, silvery scales.
- Itching and burning sensations: The affected areas may be itchy and sometimes painful.
- Dry and cracked skin: The skin may become dry, leading to cracking and bleeding.
- Thickened and pitted nails: Psoriasis can affect the nails, causing them to become thickened, ridged, or pitted.
- Joint pain and swelling: Some individuals with psoriasis may develop psoriatic arthritis, which causes joint pain, stiffness, and swelling.
Psoriasis symptoms can come and go in cycles, with periods of flare-ups followed by periods of remission. The triggers for flare-ups can vary among individuals and may include stress, infections, certain medications, cold weather, or injury to the skin.
What are the Risk Factors Associated with Psoriasis?
Psoriasis is influenced by a combination of genetic, immune system, and environmental factors. While the exact cause of psoriasis is not fully understood, several risk factors have been identified:
- Family history: Having a family member with psoriasis increases the likelihood of developing the condition.
- Genetics: Certain genes are believed to be associated with psoriasis, although having these genes does not guarantee the development of the condition.
- Immune system abnormalities: Psoriasis is considered an autoimmune disease, which means the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy cells, leading to inflammation and the rapid growth of skin cells.
- Environmental factors: Certain environmental factors, such as infections (such as streptococcal throat infection), injuries to the skin, and stress, can trigger or worsen psoriasis symptoms in susceptible individuals.
- Obesity: Being overweight or obese increases the risk of developing psoriasis. The exact reasons for this association are not yet fully understood.
- Smoking and alcohol consumption: Both smoking and excessive alcohol consumption have been linked to an increased risk of developing psoriasis, as well as worsening its severity.
It's important to note that while these risk factors are associated with an increased likelihood of developing psoriasis, not everyone with these risk factors will develop the condition. Psoriasis is a complex condition with various contributing factors, and further research is needed to fully understand its development and progression.
Prevention of Psoriasis
While psoriasis cannot be completely prevented, certain lifestyle changes and strategies may help in managing the condition and reducing the frequency and severity of flare-ups. Here are some preventive measures that may be beneficial:
- Maintain a healthy weight: Obesity has been linked to an increased risk of psoriasis and may worsen existing symptoms. Aim to maintain a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular physical activity.
- Manage stress: Stress can trigger or aggravate psoriasis symptoms. Explore stress management techniques such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, yoga, or engaging in hobbies and activities that help you relax.
- Avoid skin injuries: Injuries to the skin, such as cuts, burns, or insect bites, can trigger psoriasis flare-ups. Take precautions to protect your skin and avoid potential injuries.
- Limit alcohol consumption: Excessive alcohol consumption has been associated with an increased risk of psoriasis and may worsen symptoms. If you drink alcohol, do so in moderation or consider avoiding it altogether.
- Quit smoking: Smoking has been linked to a higher risk of developing psoriasis and may also worsen existing symptoms. If you smoke, seek support and resources to quit smoking.
- Protect your skin from the sun: Sunburn can trigger psoriasis flares, while sunlight in moderation may improve symptoms for some individuals. Find a balance and use sunscreen, protective clothing, and seek shade when necessary.
It's important to note that these preventive measures may vary in effectiveness for each individual. Consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice and guidance in managing and preventing psoriasis.
Are there any Lifestyle Changes that can Help Prevent Psoriasis?
While psoriasis cannot be completely prevented, certain lifestyle changes may help in managing the condition and reducing the frequency and severity of flare-ups. Here are some lifestyle changes that can be beneficial:
- Maintain a healthy weight: Obesity is associated with an increased risk of psoriasis and may exacerbate existing symptoms. Adopting a balanced diet and engaging in regular physical activity can help maintain a healthy weight.
- Manage stress: Stress can trigger or worsen psoriasis symptoms. Incorporating stress management techniques such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, or engaging in activities that promote relaxation can be helpful.
- Avoid skin injuries: Skin injuries like cuts, scrapes, or burns can trigger psoriasis flare-ups. Taking precautions to protect the skin and practicing good wound care can minimize the risk of exacerbations.
- Limit alcohol consumption: Excessive alcohol consumption has been linked to an increased risk of psoriasis and may worsen symptoms. It is advisable to consume alcohol in moderation or consider abstaining from it.
- Quit smoking: Smoking has been associated with a higher risk of psoriasis and may also worsen existing symptoms. Quitting smoking can have a positive impact on overall health and potentially reduce psoriasis severity.
- Protect your skin from the sun: Sunburn can trigger psoriasis flares, while controlled exposure to sunlight may help alleviate symptoms for some individuals. Using sunscreen, wearing protective clothing, and seeking shade when necessary can protect the skin.
It's important to note that while these lifestyle changes may help manage psoriasis, they may vary in effectiveness for each individual. Consulting with a healthcare professional is recommended to develop a personalized approach to prevent and manage psoriasis.
Can Stress Management Techniques Contribute to the Prevention of Psoriasis?
While psoriasis cannot be completely prevented, stress management techniques can play a significant role in managing the condition and potentially reducing the frequency and severity of flare-ups. Here's how stress management techniques can contribute:
- Reducing triggers: Stress is known to trigger or worsen psoriasis symptoms. By effectively managing stress, individuals may be able to reduce the triggers that lead to flare-ups.
- Improving immune function: Chronic stress can weaken the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to psoriasis. Implementing stress management techniques can help improve immune function and potentially reduce the risk of developing psoriasis or its severity.
- Promoting overall well-being: Stress management techniques, such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, or engaging in enjoyable activities, can promote relaxation and overall well-being. This can have a positive impact on both mental and physical health, potentially improving psoriasis symptoms.
- Enhancing treatment outcomes: Managing stress alongside medical treatment can enhance the effectiveness of psoriasis therapies. By reducing stress levels, individuals may experience better response to treatment and improved management of their condition.
It's important to note that while stress management techniques can be beneficial, they may not completely prevent psoriasis or eliminate all flare-ups. Psoriasis is a complex condition influenced by various factors, and a comprehensive approach that includes stress management, lifestyle changes, and medical treatment may be necessary for optimal management.
Is there a Link between Diet and the Prevention of Psoriasis?
While diet alone cannot prevent psoriasis, certain dietary choices may have an impact on managing the condition and reducing the frequency and severity of flare-ups. Here are some points to consider regarding the link between diet and psoriasis:
- Anti-inflammatory foods: Some evidence suggests that incorporating anti-inflammatory foods, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, fatty fish, and healthy fats like olive oil, may help reduce inflammation in the body, potentially benefiting individuals with psoriasis.
- Weight management: Maintaining a healthy weight is important for managing psoriasis as obesity has been linked to an increased risk and severity of the condition. Following a well-balanced diet and engaging in regular physical activity can support weight management.
- Identifying trigger foods: While there is no specific psoriasis diet, some individuals may find that certain foods trigger or worsen their symptoms. It can be helpful to identify and avoid such trigger foods based on personal experience or under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
- Vitamin and nutrient intake: Adequate intake of vitamins and nutrients, such as vitamin D, omega-3 fatty acids, and antioxidants, may be beneficial for overall skin health. However, it's important to discuss any dietary supplements or major diet changes with a healthcare professional before implementing them.
- Individual variations: It's important to recognize that the impact of diet on psoriasis can vary among individuals. What works for one person may not work for another. It's recommended to consult with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian for personalized dietary advice.
It's worth noting that while diet can potentially play a role in managing psoriasis, it should not replace medical treatment or other recommended interventions. A holistic approach that combines a healthy diet, stress management, lifestyle modifications, and appropriate medical care is typically the most effective strategy for managing psoriasis.
Treatment Options for Psoriasis
Psoriasis is a chronic condition that requires ongoing management. Various treatment options are available to help alleviate symptoms and control the disease. The choice of treatment depends on the severity of the condition, individual factors, and the preferences of the patient. Here are some common treatment options for psoriasis:
- Topical treatments: These medications are applied directly to the skin and can help reduce inflammation, itching, and scaling. Examples include corticosteroids, vitamin D analogs, retinoids, salicylic acid, and moisturizers.
- Phototherapy: This treatment involves exposing the skin to ultraviolet (UV) light under medical supervision. Phototherapy can help slow down the excessive growth of skin cells and reduce inflammation. Different types of phototherapy include UVB therapy, PUVA (psoralen plus ultraviolet A) therapy, and excimer laser therapy.
- Systemic medications: For moderate to severe psoriasis, oral or injectable medications may be prescribed. These medications work throughout the body to suppress the immune system and reduce inflammation. Examples include methotrexate, cyclosporine, acitretin, and biologics.
- Combination therapy: In some cases, a combination of treatments may be recommended to achieve better results. For example, combining topical treatments with phototherapy or combining systemic medications with phototherapy.
- Lifestyle modifications: Certain lifestyle changes can complement medical treatments and help manage psoriasis. These include stress management, maintaining a healthy weight, avoiding triggers, and protecting the skin from excessive dryness or injury.
- Supportive care: Psoriasis can have a significant impact on a person's psychological well-being. Seeking support from healthcare professionals, joining support groups, and practicing self-care can be beneficial in coping with the emotional aspects of the condition.
It's essential to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most suitable treatment options based on individual needs and circumstances. Treatment plans may need to be adjusted over time to ensure optimal management of psoriasis.
Traditional Treatment Approaches for Psoriasis
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune skin condition that has been treated using various traditional approaches over the years. While newer treatment options are available, traditional methods still play a significant role in managing the disease. Here are some commonly used traditional treatment approaches for psoriasis:
- Topical medications: Traditional topical treatments for psoriasis include corticosteroids, coal tar, and anthralin. These medications are applied directly to the affected skin to reduce inflammation, itching, and scaling.
- Ultraviolet (UV) light therapy: Phototherapy, using UV light, is a traditional treatment approach for psoriasis. Narrowband UVB therapy and PUVA (psoralen plus ultraviolet A) therapy are commonly used to slow down the excessive growth of skin cells and reduce inflammation.
- Systemic medications: Traditional systemic medications used for psoriasis include methotrexate, cyclosporine, and acitretin. These medications work throughout the body to suppress the immune system and reduce inflammation.
- Coal tar preparations: Coal tar has been a traditional remedy for psoriasis for many years. Coal tar preparations, such as creams, ointments, and shampoos, can help reduce scaling, itching, and inflammation.
- Salicylic acid: Salicylic acid is a traditional keratolytic agent used to remove scales and promote the effectiveness of other treatments. It is often combined with other medications or included in shampoos, creams, or lotions.
- Moisturizers: Keeping the skin moisturized is an essential part of managing psoriasis. Traditional moisturizers, such as emollients and humectants, help alleviate dryness, reduce itching, and improve the overall appearance of the skin.
While traditional treatment approaches have been effective for many individuals, it's important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most suitable options and to ensure proper monitoring and management of the condition.
Latest Advancements in Psoriasis Treatment
Psoriasis treatment has seen significant advancements in recent years, offering new options for managing the condition. These advancements are aimed at improving the effectiveness of treatment, minimizing side effects, and enhancing the overall quality of life for individuals with psoriasis. Here are some of the latest advancements in psoriasis treatment:
- Biologic therapies: Biologic medications are a major breakthrough in psoriasis treatment. They are designed to target specific components of the immune system involved in psoriasis, such as tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha), interleukin-17 (IL-17), and interleukin-23 (IL-23). Biologics can effectively control psoriasis symptoms and reduce inflammation.
- Targeted therapies: Targeted therapies aim to block specific molecules or pathways involved in the development of psoriasis. Drugs targeting molecules like phosphodiesterase-4 (PDE-4) and Janus kinase (JAK) have shown promising results in clinical trials, providing new treatment options.
- Small molecule inhibitors: Small molecule inhibitors are oral medications that target specific molecules involved in the immune response. They offer an alternative to injectable biologics and have shown efficacy in treating psoriasis, particularly in individuals who may prefer oral medications.
- Advanced phototherapy: Phototherapy techniques have evolved to become more targeted and precise. Excimer laser therapy, for example, delivers focused UVB light to affected areas, minimizing exposure to healthy skin. This approach allows for shorter treatment sessions and potentially better outcomes.
- Personalized medicine: Advancements in genetic research and understanding of individual variability have paved the way for personalized medicine in psoriasis treatment. Genetic testing and biomarker analysis can help determine an individual's response to specific treatments, allowing for tailored and more effective therapeutic approaches.
- Combined therapies: Combining different treatment modalities, such as biologics with topical medications or phototherapy, has shown enhanced efficacy in managing psoriasis. Combination therapies can target multiple factors contributing to the disease and provide better control of symptoms.
These latest advancements in psoriasis treatment offer hope for improved outcomes and better disease management. However, it's important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most suitable treatment approach based on individual needs and circumstances.
How can topical treatments effectively manage psoriasis?
Psoriasis is a chronic skin condition that can be effectively managed using topical treatments. These medications are applied directly to the affected areas of the skin and can help reduce inflammation, control symptoms, and improve the overall appearance of the skin. Here are some ways in which topical treatments can effectively manage psoriasis:
- Reducing inflammation: Topical treatments, such as corticosteroids or vitamin D analogs, can help suppress the immune response in the skin, reducing inflammation and slowing down the excessive growth of skin cells characteristic of psoriasis.
- Relieving itching and scaling: Itching and scaling are common symptoms of psoriasis. Topical treatments containing ingredients like salicylic acid or coal tar can help soothe itching and promote the shedding of scales, leading to symptom relief.
- Moisturizing the skin: Psoriasis often leads to dry, flaky skin. Moisturizers, including emollients and humectants, can help hydrate the skin, improve its barrier function, and reduce dryness and itchiness.
- Enhancing the effectiveness of other treatments: Topical treatments can be used in combination with other treatment modalities, such as phototherapy or systemic medications, to enhance their effectiveness. Using topical treatments alongside other therapies can provide better control of symptoms.
- Providing localized treatment: Topical treatments are directly applied to the affected areas, allowing for targeted treatment. This localized approach can be beneficial in managing psoriasis plaques and minimizing the potential side effects associated with systemic treatments.
- Convenience and ease of use: Topical treatments are often available as creams, ointments, gels, or foams, which are easy to apply and integrate into daily skincare routines. They provide a convenient and accessible option for managing mild to moderate psoriasis.
It's important to note that the effectiveness of topical treatments may vary depending on the individual and the severity of the psoriasis. Consulting with a healthcare professional is essential to determine the most suitable topical treatments and develop an individualized treatment plan.
Systemic Treatment Options for Psoriasis
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune condition that may require systemic treatments to manage symptoms and control the underlying immune response. Systemic medications work throughout the body to suppress the immune system and reduce inflammation associated with psoriasis. Here are some systemic treatment options available for psoriasis:
- 1. Conventional oral medications: Traditional oral medications such as methotrexate, cyclosporine, and acitretin have been used for years to treat moderate to severe psoriasis. These medications help slow down the growth of skin cells and reduce inflammation.
- 2. Biologic therapies: Biologics have revolutionized psoriasis treatment. These medications target specific components of the immune system involved in psoriasis, such as tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha), interleukin-17 (IL-17), and interleukin-23 (IL-23). Biologics are administered by injection or infusion and effectively control symptoms and reduce inflammation.
- 3. Oral small molecule inhibitors: Small molecule inhibitors like apremilast and tofacitinib are newer systemic treatments for psoriasis. They work by targeting specific molecules involved in the immune response. These oral medications provide an alternative to biologics for individuals who prefer oral administration.
- 4. Systemic retinoids: Systemic retinoids, such as acitretin, are derived from vitamin A and have been used to treat severe psoriasis. They help normalize skin cell growth and reduce inflammation, but they may have side effects that require careful monitoring.
- 5. Immunomodulatory drugs: Drugs like apremilast modulate the immune system to reduce inflammation and control psoriasis symptoms. They are taken orally and are particularly useful for individuals with moderate to severe psoriasis who are unable to use or have failed other systemic treatments.
- 6. Combination therapies: Combining different systemic medications, such as biologics with oral medications, can enhance their effectiveness in managing psoriasis. Combination therapies are often used for individuals with severe or treatment-resistant psoriasis.
Each systemic treatment option has its benefits and considerations. It's important to consult with a healthcare professional who can evaluate individual needs and determine the most appropriate systemic treatment plan for psoriasis management.
Q1:
What is Psoriasis, and what are its common symptoms?
A1:
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune skin condition characterized by the rapid buildup of skin cells, resulting in thick, red, scaly patches known as plaques. Common symptoms include red patches of skin covered with silvery scales, itching, burning sensations, dry and cracked skin, thickened and pitted nails, and in some cases, joint pain and swelling.
Q2:
What are the risk factors associated with Psoriasis?
A2:
Psoriasis is influenced by a combination of genetic, immune system, and environmental factors. Risk factors include a family history of psoriasis, certain genetic predispositions, immune system abnormalities, environmental triggers like infections, injuries to the skin, stress, obesity, and habits like smoking and excessive alcohol consumption.
Q3:
How can psoriasis be prevented or managed?
A3:
While psoriasis cannot be completely prevented, certain lifestyle changes and strategies can help manage the condition. These include maintaining a healthy weight, managing stress, avoiding skin injuries, limiting alcohol consumption, quitting smoking, and protecting the skin from excessive sun exposure. Consultation with a healthcare professional is recommended for personalized guidance.
Q4:
What are the latest advancements in psoriasis treatment?
A4:
Recent advancements in psoriasis treatment include biologic therapies that target specific immune components, targeted therapies blocking specific molecules, small molecule inhibitors, advanced phototherapy techniques, personalized medicine, and combination therapies. These innovations aim to improve treatment effectiveness, minimize side effects, and enhance the quality of life for individuals with psoriasis.
Q5:
How can topical treatments effectively manage psoriasis?
A5:
Topical treatments can effectively manage psoriasis by reducing inflammation, relieving itching and scaling, moisturizing the skin, enhancing the effectiveness of other treatments, providing localized treatment, and offering convenience and ease of use. These treatments can be tailored to individual needs and are commonly used for mild to moderate psoriasis.