Explore the answers to What kills off acne? and discover proven strategies to achieve a blemish-free complexion Our comprehensive guide reveals the secrets to combat acne effectively
What kills off acne? This is a common question for individuals seeking clear and healthy skin. Acne can be a persistent and frustrating skin condition, but there are effective ways to combat it. Whether you're dealing with occasional breakouts or more severe acne issues, understanding the causes and treatments can help you achieve the acne-free complexion you desire. In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore the factors contributing to acne and the various methods to effectively eliminate it, giving you the knowledge and tools to regain confidence in your skin's appearance.
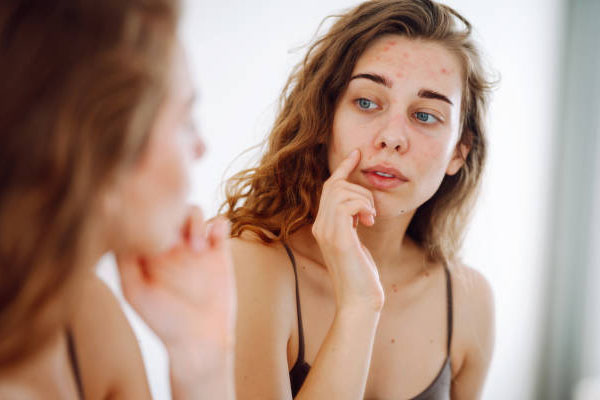

Understanding Acne
Acne is a common skin condition characterized by the presence of pimples, blackheads, whiteheads, and sometimes cysts or nodules. Understanding the basics of acne is essential for effective treatment and prevention.
Common Causes of Acne
Understanding the common causes of acne is essential for effective treatment and prevention. Acne can be triggered by various factors, and each individual may experience it differently. Here are some of the most prevalent causes:
- Excess Oil Production: One of the primary culprits is the overproduction of sebum, a natural oil that lubricates the skin. When the sebaceous glands produce too much oil, it can clog hair follicles, leading to acne development.
- Clogged Pores: When hair follicles become clogged with a combination of oil and dead skin cells, it creates an environment for the growth of bacteria, resulting in acne lesions.
- Bacterial Growth: Propionibacterium acnes (P. acnes) is a type of bacteria that resides on the skin's surface. When this bacterium proliferates within clogged pores, it triggers inflammation, leading to the formation of acne.
- Hormonal Fluctuations: Hormonal changes, particularly during puberty, the menstrual cycle, and pregnancy, can stimulate the sebaceous glands to produce more oil. This makes individuals more prone to acne breakouts.
- Genetics: Family history can play a significant role. If your parents had acne, you may be more likely to develop it as well.
It's important to note that while these are common causes, various other factors, such as diet, stress, and environmental factors, can also contribute to acne development. Understanding the root causes of your acne can help tailor a more effective treatment and prevention plan.
Medical Treatments for Acne
While over-the-counter remedies can be effective for mild cases of acne, medical treatments offer more powerful options for those with moderate to severe acne. Consulting a dermatologist can help you explore the most suitable medical treatments for your specific condition. Here are some of the medical treatments commonly used to combat acne:
- Topical Treatments: Dermatologists often prescribe topical treatments that can be applied directly to the skin. These may include retinoids, antibiotics, or combination medications to unclog pores and reduce inflammation.
- Oral Medications: For more severe cases, oral antibiotics like tetracycline or doxycycline may be recommended to target bacteria and reduce inflammation. In some instances, oral contraceptives may also be prescribed for females to regulate hormonal fluctuations that can lead to acne.
- Isotretinoin (Accutane): Isotretinoin is a potent oral medication used to treat severe cystic acne. It works by shrinking the sebaceous glands, reducing oil production, and preventing clogged pores. It is highly effective but can have side effects and requires close monitoring by a healthcare provider.
- Laser and Light Therapies: Various laser and light-based treatments are available to target acne. These therapies aim to destroy the bacteria causing acne and reduce inflammation. They can also improve the appearance of acne scars.
- Chemical Peels: Chemical peels involve the application of a chemical solution to the skin, which exfoliates the top layer, helping to unclog pores and reduce the appearance of acne. They can also enhance the texture and tone of the skin.
It's important to consult with a dermatologist to determine the most appropriate medical treatment based on the type and severity of your acne. Medical treatments are typically more effective but may also come with potential side effects, so professional guidance is crucial to ensure safe and successful acne management.
Preventing Acne Breakouts
Preventing acne breakouts is crucial for maintaining clear and healthy skin. While there is no foolproof method to completely eliminate the risk of acne, there are several effective strategies that can significantly reduce the frequency and severity of breakouts. Here are some key practices to prevent acne:
- Proper Skincare: Establish a consistent skincare routine that includes gentle cleansing and moisturizing. Use products that are suitable for your skin type, and avoid harsh scrubs that can irritate the skin.
- Avoid Touching Your Face: Touching your face with your hands or allowing your phone, hats, or other objects to come into contact with your skin can transfer dirt, oil, and bacteria, contributing to acne. Keep your hands away from your face and regularly clean items that touch your skin.
- Healthy Diet: A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains can promote skin health. Limit the consumption of high-sugar and high-fat foods, as they may exacerbate acne.
- Stay Hydrated: Proper hydration is essential for skin health. Drinking an adequate amount of water can help flush toxins from your body and keep your skin well-hydrated.
- Manage Stress: Stress can trigger hormonal changes that may lead to acne breakouts. Practicing stress management techniques such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing can be beneficial.
- Avoid Overexposure to Sun: While some sun exposure can initially improve acne, excessive sun exposure can cause skin damage and worsen acne in the long run. Use sunscreen and protective clothing when spending time outdoors.
It's essential to understand that preventing acne may require patience, as it can take time to see results. Additionally, individual responses to preventive measures may vary. If you continue to experience persistent or severe acne, it's advisable to seek professional guidance from a dermatologist to explore more advanced preventive strategies and treatment options.
FAQs about Acne
Q1: What causes acne breakouts?
A1: Acne breakouts are primarily caused by factors such as excess oil production, clogged pores, bacterial growth, hormonal fluctuations, and genetics.
Q2: Are there effective over-the-counter treatments for acne?
A2: Yes, over-the-counter treatments like benzoyl peroxide, salicylic acid, and sulfur-based products can be effective for mild cases of acne. However, for moderate to severe acne, it's advisable to consult a dermatologist for medical treatments.
Q3: Can hormonal changes trigger acne breakouts?
A3: Yes, hormonal fluctuations, particularly during puberty, the menstrual cycle, and pregnancy, can stimulate the sebaceous glands to produce more oil, making individuals more prone to acne breakouts.
Q4: Is there a one-size-fits-all treatment for acne?
A4: No, the most effective acne treatment can vary depending on an individual's unique condition. Consultation with a dermatologist is essential to determine the most suitable treatment plan.
Q5: Can diet affect acne breakouts?
A5: Yes, diet can play a role in acne. A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can promote skin health, while high-sugar and high-fat foods may exacerbate acne in some individuals.
Q6: What is the role of genetics in acne development?
A6: Genetics can influence the likelihood of developing acne. If your parents had acne, you may be more predisposed to it.
Q7: Are there side effects associated with acne medications?
A7: Some acne medications, especially oral ones like isotretinoin, may have side effects. It's crucial to discuss potential side effects with your healthcare provider and follow their recommendations closely.
Q8: Can stress contribute to acne breakouts?
A8: Yes, stress can trigger hormonal changes that may lead to acne breakouts. Managing stress through relaxation techniques can be beneficial.
Q9: What are the most effective ways to prevent acne breakouts?
A9: Effective prevention measures include proper skincare, avoiding touching your face, maintaining a healthy diet, staying hydrated, managing stress, and protecting your skin from excessive sun exposure.
Q10: When should I seek professional help for acne?
A10: If you continue to experience persistent or severe acne that does not respond to over-the-counter treatments, it's advisable to consult a dermatologist for advanced preventive and treatment strategies.